What is Component Testing?
When examined from an architectural standpoint, it is also known as module testing. Unit testing, program testing, and module testing are other names for component testing.
Any software is often composed of multiple components. Testing each of these components separately is the focus of component level testing.Component testing is defined as a software testing type, in which the testing is performed on each individual component separately without integrating with other components
It's one of the black box testing kinds that the QA Team does the most frequently.
There will be a test strategy and test plan for component testing, as shown in the picture below. where each component of the program or application is taken into account separately.
A test scenario will be built for each of these components, and it will be further broken down into High Level Test Cases -> Low Level detailed Test Cases with Prerequisites.
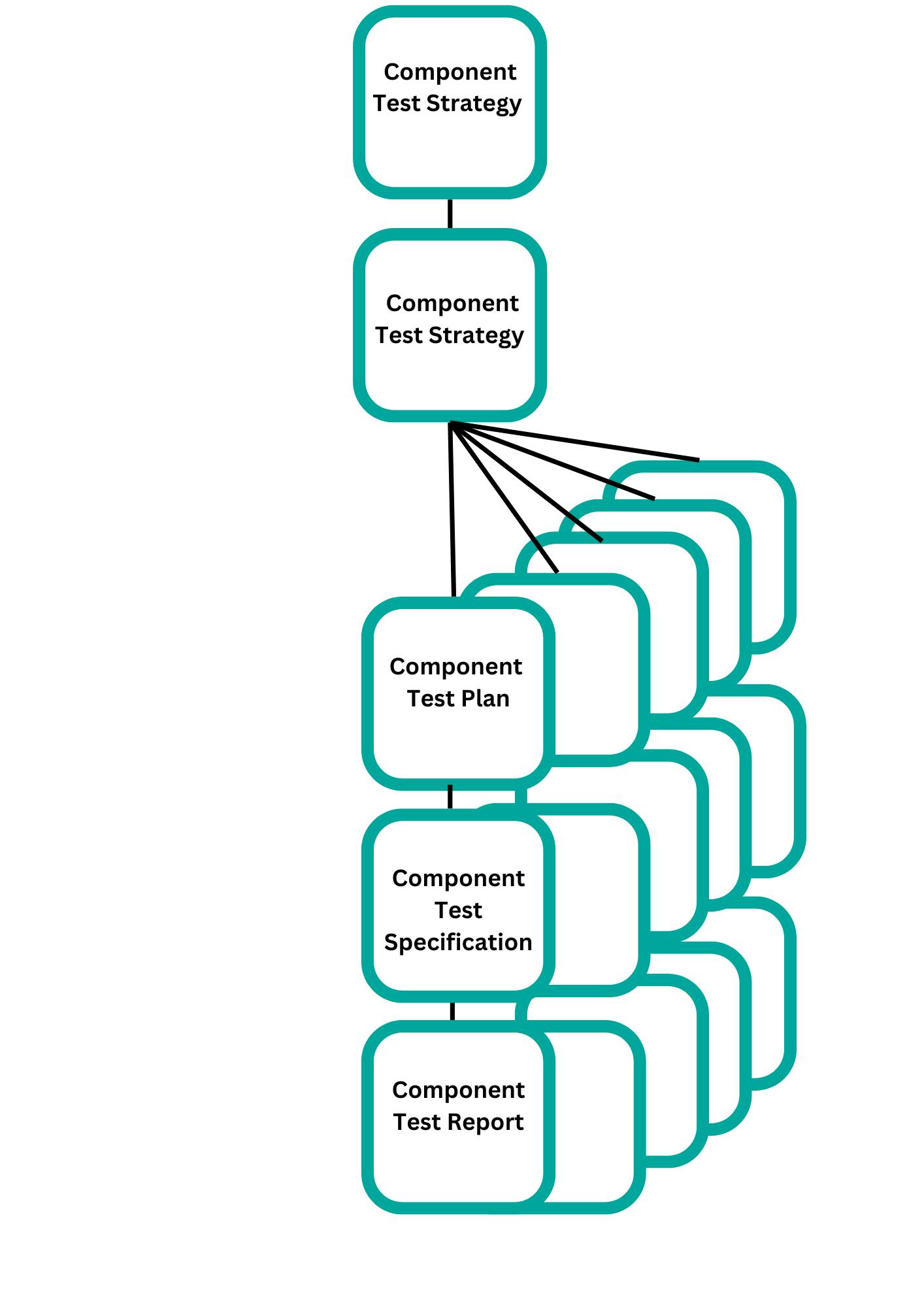
Testing separate components of the software
There are several types of Component Testing, each serving a specific purpose in the software testing process:
Unit Testing
Unit Testing is the most common type of Component Testing, focusing on testing individual units or functions within a component. It ensures that each unit performs as expected and meets the defined requirements.
Integration Testing
Integration Testing involves testing the interaction between different components or modules to ensure they work together seamlessly. It verifies the correct integration of components and identifies any issues that may arise during the integration process.
Mock Testing
Mock Testing is used to simulate the behavior of dependent components that are not yet available for testing. Mock objects are created to mimic the behavior of these components, allowing testing to proceed without dependencies.
Stub Testing
Stub Testing is similar to Mock Testing but focuses on testing components that depend on other components. Stubs are used to replace the dependencies and provide predetermined responses, allowing the testing of the dependent component.
Component Interface Testing
Component Interface Testing verifies the communication and interaction between different components. It ensures that the interfaces between components are well-defined and function correctly.
Who does Component Testing
| Developers' Role | Testing Team's Role |
| Designing and implementing individual components, such as modules, units, programs, functions, or classes. | Performing broader component tests that go beyond individual units, checking the integration and interactions between different components. |
| Creating and executing unit tests to verify the correctness of each component in isolation. | Using testing tools like stubs, simulators, or drivers to replace components and validate their interactions. |
| Ensuring that the components meet the specified requirements and function as intended. | Identifying and reporting defects or issues found during component testing. |
| Collaborating with developers to ensure comprehensive test coverage and effective issue resolution. |
When to perform Component testing
Component testing is strategically conducted at specific stages within the software development lifecycle. Understanding the appropriate timing is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness.
Entry criteria
Before initiating component testing, certain conditions or criteria need to be met:
Completion of Unit Testing
- Component testing typically follows unit testing, ensuring that individual components have undergone thorough examination.
Availability of Components
- The components to be tested should be developed and ready for evaluation.
Exit criteria
Component testing concludes based on predefined criteria:
Comprehensive Test Coverage
- Ensure that component testing covers all the specified modules, units, programs, functions, or classes.
Documentation
- Adequate documentation of test cases, results, and any modifications made during testing
Component Testing Techniques
Component testing, based on the depth of testing levels, can be categorized into two distinct approaches: CTIS (Component Testing In Small) and CTIL (Component Testing In Large).
CTIS - Component Testing In Small
CTIS focuses on the meticulous examination of individual components at a granular level. This approach involves testing components such as modules, units, programs, functions, or classes in isolation. Key aspects of CTIS include:
Unit Testing
Isolation Testing
Stub Implementation
CTIL - Component Testing In Large
CTIL extends the scope of testing to assess the integration and interactions of multiple components within a larger context. This approach involves testing components collectively to ensure seamless collaboration. Key aspects of
Integration Testing
Driver Implementation
Interaction Testing.
Unit Testing Vs Component Testing Table
| Criteria | Unit Testing | Component Testing |
| Scope | Individual functions, methods, or procedures. | Modules, units, programs, functions, or classes. |
| Dependencies | Typically tested in isolation. | May involve testing interactions with other components. |
| Test Purpose | Verify the correctness of each unit. | Verify the integration and interactions of components. |
| Testing Tools | Mocks and stubs are commonly used. | Stubs, simulators, or drivers are used. |
| Responsibility | Developers often perform unit testing. | Testing team or developers can perform component testing. |
| Timing | Conducted during the development phase. | Conducted after unit testing and before integration testing. |
Example Test Cases for Component Testing
Test Case 1: Input Validation
Test if the component correctly validates input data for expected formats and constraints.
Verify the component's behavior when invalid or unexpected input is provided.
Test Case 2: Boundary Testing
Test the component's behavior at the lower and upper boundaries of input values.
Verify if the component handles boundary conditions correctly and produces the expected output.
Test Case 3: Error Handling
Test the component's error handling capabilities by providing erroneous input or triggering error conditions.
Verify if the component gracefully handles errors and produces appropriate error messages or responses.
Test Case 4: Performance Testing
Test the performance of the component under different load conditions.
Verify if the component meets the specified performance requirements and responds within acceptable time limits.
Test Case 5: Compatibility Testing
Test the component's compatibility with different operating systems, browsers, or hardware configurations.
Verify if the component functions correctly across various platforms and configurations.
Summary:
Component testing focuses on testing individual components such as modules, units, programs, functions, or classes. It involves the use of stubs and drivers to replace components and verify their interactions.
This testing is performed after unit testing and before integration testing, with specific entry and exit criteria in place. Various testing techniques, including static and dynamic testing, can be applied during component testing to ensure the reliability and correctness of individual components.
References
[1] S. Kaner, J. Falk, and H. Q. Nguyen, "Testing Computer Software," Wiley, 1999. [2] M. J. Whittaker, "How to Break Software: A Practical Guide to Testing," Addison-Wesley Professional, 2002. [3] G. Myers, "The Art of Software Testing," Wiley, 2004.
